Modalities of Teaching
The goal of teaching is to empower students by facilitating their understanding, promoting critical thinking, fostering skill development, cultivating curiosity and lifelong learning, supporting personal growth, empowering individual potential, and creating inclusive and supportive learning environments, thereby preparing them to become knowledgeable, competent, compassionate, and engaged individuals ready to contribute positively to society.
Teaching has 4 modes of behaviour or we can say it has 4 modalities. It means that teaching is a continuum for developing behaviour to the formation of beliefs. Thus, teaching is a continuum from conditioning to indoctrination.
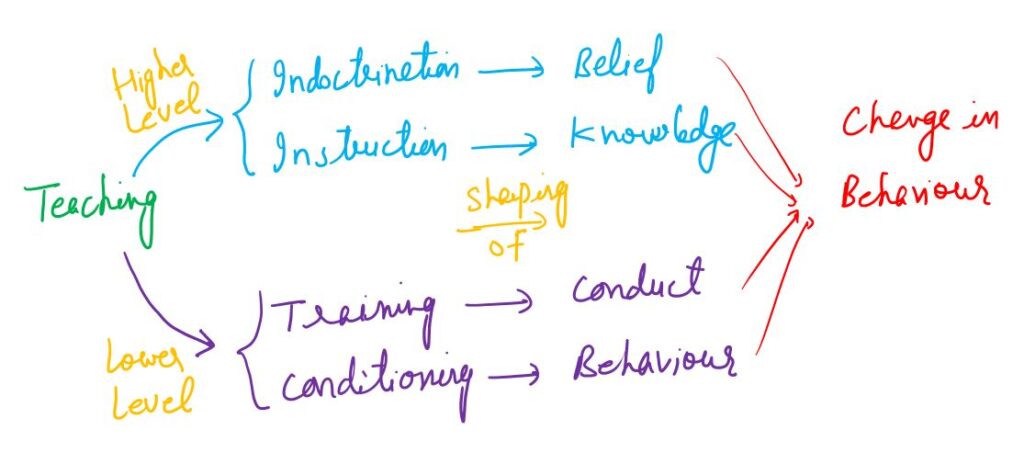
The 4 modalities of teaching are given below.
1. Conditioning
It aims at modification of behaviour and learning habits. This is the lowest level or mode of teaching. For example, many of the animals and human beings may be taught to respond to signals, alarms, signs and warnings through conditioning. Most of our desirable or undesirable behaviours and habits are the creation of the process of conditioning.
2. Training
It is concerned with a little more raised level of teaching than conditioning. It helps in shaping conduct and teaching various skills. For example, a worker may be trained to perform certain tasks requiring very specific skills by giving him desired knowledge of the machine, its operation and mechanism.
3. Instruction
Instruction, in brief, is mainly concerned with the development of knowledge and understanding in an individual about a thing, system or process. For example, programmed materials, computers, teaching machines, radios, and tape recorders are used to provide directions in a classroom. In short, instruction is always a part or one of the several modes of teaching.
4. Indoctrination
It represents a fairly high level of teaching which adds to the establishment or shaping of beliefs and ideals. It requires higher order of intelligence and results in bringing quite stable changes in the cognitive and affective domains of one’s behaviour. For example, shaping political beliefs in a youth organization.
Teaching is a larger concept and each of these terms is a part or aspect of this large concept.
UGC NET Previous Year Questions (Modalities of Teaching)
1.) Match List I with List II: (22 Nov Morning 2021)
List I (Modalities of Teaching)
a. Instruction
b. Training
c. Conditioning
d. Indoctrination
List II (Implementation)
(i) One way imposition of ideas from the teacher to the students.
(ii) Associative presentation of ideas from teacher to students.
(iii) Disciplined drill conducted by teacher.
(iv) Active interchange of ideas between teacher and students.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Codes
(A) a-(ii), b-(i), c-(iv), d-(iii)
(B) a-(i), b-(ii), c-(iii), d-(iv)
(C) a-(iv), b-(iii), c-(ii), d-(i)
(D) a-(iii), b-(iv), c-(i), d-(ii)
ANS. C
2.) If teaching is viewed as a continuum, which of the following modality, involves active ‘give’ and ‘take’ between the teacher and learner? (UGC NET 5th Nov 2020 Evening paper)
(A) Training
(B) Conditioning
(C) Instruction
(D) Indoctrination
ANS. C
3.) The goal of teaching as compared to training is to provide opportunity of: (UGC NET 11th Nov 2020 Morning paper)
(A) Promotion of organized ideas as a result of disciplined drill
(B) Sharing and caring leading to critical and creative reflection
(C) Establishing beliefs and values leading to change in attitude
(D) Associating ideas which are similar and dissimilar
ANS. B
4.) Teaching differs from training and conditioning in so far as it promotes (UGC NET 25th Sept 2020 Morning paper)
(A) Disciplined drill
(B) Critical thinking
(C) Steady association
(D) Mastery of facts
ANS. B



